Wireless Internet in El Salvador
Internet usage by teens in El Salvador
Broadband connections in El Salvador
Internet navigation habits in El Salvador
Wireless Internet in El Salvador
In 2000 the first providers to offer WAP, or wireless Internet access, using mobile phones were Telefónica and Telemóvil. Due to the limitations in screen size, slow speed and high cost this service never became popular. The WAP service faced the same lack of popularity in the rest of the world as well, the reasons were probably the same.
It was until 2005 when WAP 2.0 was launched in El Salvador., this newer version of wireless Internet followed similar standards as the normal Internet network, making it more compatible and easier to develop. This service is becoming more popular, now all GSM mobile phone operators in the country offer this service. One of the main differences of WAP 1.0 with WAP 2.0 is that the latter uses a packet data transmission system instead of a normal phone call to exchange data, thus using bandwidth more effectively.
Accessing the Internet in El Salvador does not require being in a desktop computer anymore, recently Tigo, the second largest mobile phone provider in Central America, launched a wireless Internet service that is available in most of the country as well as in Honduras and Guatemala for a $15 monthly rate. This service brings the mobile's Internet connection outside the phone. With a special device provided by Tigo a laptop computer can use mobile network and connect to the Internet from most of the country. This new service uses the existing GSM mobile network with the GPRS and EDGE protocols that allow speeds of up to 100 kbps. The speeds are slower compared to wired connections, but it makes the service available anywhere.
WiFi Internet access refers to a kind of Wireless Local Area Network that is connected to the Internet. A laptop computer or a handheld computer equipped with a WiFi antenna can connect to this kind of wireless network. This service is usually available in restaurants, hotels and shopping centers. The service can either be free and run on the cost of the business providing it (an hotel for example), or be paid or subscription based like Telemovil's E-Spot or Telecom's Turbomóvil.
Internet usage by teens in El Salvador
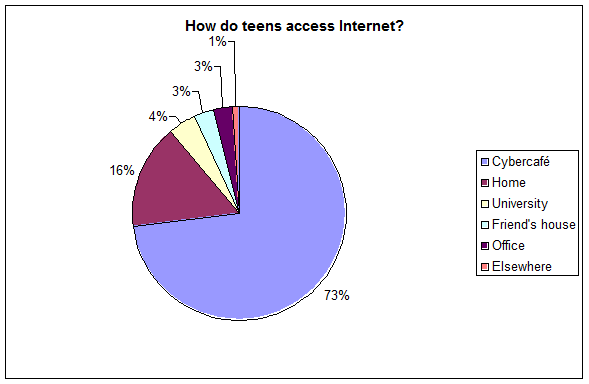
A recent investigation by El Diario de Hoy stated that teens were “more connected than ever” (2006) by using mobile phones and computers to keep in touch with each other. One of their analysis focused on determining how the Salvadoran youth connected to the Internet. The results showed that 73% connect using Cybercafés, 16% from their houses, 4% from universities, 3% from friend's houses, 3% from work and 1% from other places. The reason that such a great percentage of teens connect from Cybercafés is that they don't have Internet access at home or they don't have a computer at home.
Competition between Cybercafés has helped to keep the prices of this service low, usually ranging from $0.50 to $1.00 an hour. Another factor that contributes to the opening of many cybercafés is that they do not need a special license to open, in some countries like China or Costa Rica cybercafés follow stricter regulations.
Broadband connections in El Salvador
As mentioned before, the two most used broadband are Cable and ADSL. The ADSL Internet access provided by Telecom. ADSL works by using the entire data transmission capacity of the phone lines. The main disadvantage of ADSL is that quality of service decreases with distance, typically the maximum distance is 5 km. So far this is the most common and widely available method for connecting to the Internet.
Cable Internet works uses frequencies ranging from 5500 Mhz to 700 Mhz that are left unused by TV channels on coaxial cables. The main difference between Cable Internet and ADSL is that in Cable Internet all the users connected to the same headend will share the cable. Speed could be considerably lowered in a neighbourhood by users who constantly use the available bandwidth. In Cable Internet service having good connection speed one moment does not guarantee that the service will be excellent the next moment, everything depends on how many users are active.
Fiber Optic Internet access is only used by large companies and the telecommunications operators. Companies like AMNET, Telefónica and Telecom own fiber optic networks that connect El Salvador networks with the neighbouring countries of Honduras and Guatemala. Fiber Optics can transmit data at rates of up to 10 Gbps. In contrast with the previous two technologies that use radio frequencies, Fiber optics use light to transmit information.
Internet navigation habits in El Salvador
In El Salvador, as in most of the countries, the Internet is used by all age groups, especially the youth. Far from its first purpose of being the military and scientific network
The top-5 most visited websites in El Salvador are: MSN.com, Yahoo.com, Hi5.com and Youtube.com. None of them are Salvadoran. The highest ranked Salvadoran website is LaPrensaGrafica.com in the 14th position, followed by El DiariodeHoyon the 16th.
The previous statistics show that most of the time Salvadorans visit the Internet for Social Networking, watching videos, checking their e-mail, and reading news.
“Web 2.0” in El Salvador
Web 2.0 refers to the second-generation of the Internet, in which the user has much more opportunities to participate. The Web 2.0 doesn't refer to a technical update on how the World Wide Web works, it refers to the new usage that developers have given to the Internet. The term Web 2.0 was coined by O'Reilly Publishing in 2004, the use of the term is widespread even though the definition isn't exact. Some important characteristics of Web 2.0 are:
Sites that are examples of the so called Web2.0 are:
The effects of Web 2.0 can be seen in El Salvador too:
The second most visited website in the country is Hi5.com, a social networking website in which users publish profiles, photos, and videos and are connected to each other via his friends who form his or her “social network”. Other popular social networking websites on the Top 100 list are MySpace.com and Facebook.com.
Youtube is the fifth most visited website in El Salvador in which members from all over the world are able to publish videos that everyone can see, tag and comment.
The ninth most visited website is Wikipedia.org. The community based encyclopedia in which the articles are written by its users, and anyone can edit the articles to add them more information.
This year, LaPrensaGráfica.com the most visited newspaper website in El Salvador created a web-blogging section from topics ranging from photo-periodism to migration. It also started providing RSS feeds for its news. The fourteenth most visited website is Blogger.com, a popular web-blogging website.
Author: Rodrigo Noyola
Title: Development of the Internet in El Salvador
Published: Monday, May 14th 2007